Naevi Meaning
When diagnosing melanocytic nevus they are mainly looking to make sure if the mole is non-cancerous or cancerous in order to start the proper treatment. When you have a mole removed it is examined under a microscope. Or maybe you were not satisfied with your doctor’s response to “What is a precancerous mole? What does atypical mean?” I consulted with Maria M. Tsoukas, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor, Dermatology Section, University of Chicago, to explore in more detail just what a precancerous (atypical) mole means. First of all, if you’re concerned about a precancerous or “atypical” mole, make.
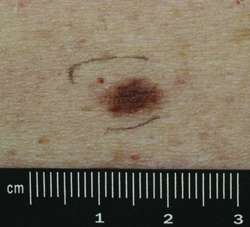
.AMN may be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait or occur sporadically - clinical and histological appearances of AMN occurring in a familial setting appear to overlap with those occurring sporadically.It is likely that both genetics and UV radiation have a role to play in their development.The prevalence of AMN in white populations has been reported to be between 2-5%. Celtic patients are much more prone to developing AMN, whereas AMN are rare in black, Asian or Middle Eastern populations.It is very difficult to assess the risk of individual atypical naevi, however, the risk of solitary lesions transforming to melanoma is very low. As the number of atypical naevi increases so does the level of risk, the presence of five atypical moles represents a relative risk of 6.36 (range 3.8-10.33) for the development of melanomaHistory. Clinical examination. Distribution.Can arise on any body site although they are most commonly found on the trunk, upper limbs, scalp and buttocks. Morphology. Size - tend to be large, commonly more than 7 mm in diameter.
Shape and border - borders often irregular resulting in unusual shapes. Colour - can vary from light-dark brown, pink and occasionally black. May be single colour or variegated. Can have an erythematous edgeDermoscopic features.In patients with several lesions they will often show a similar pattern.Beware of a lesion looking different to the others.As discussed in the chapter Melanoma - an overview the dermoscopic examination of melanocytic lesions requires considerable experience, accordingly any lesion found to have clinical OR dermoscopic features suspicious of melanoma should be referred urgently to Secondary Care as a 2 Week Rule.For more information refer to the section onImagesPlease click on images to enlarge or download.
The PCDS would like to thank Dermatoweb, DermQuest (Galderma), and others who have contributed images. All named individuals and organisations maintain copyright for the relevant images. This website is non-profit and holds the images for educational purposes only. Any image downloaded must only be used for teaching purposes and not for commercial use. Notice and credit must be given to the PCDS or other named contributor.
Many folks looking for vacation log homes have fond memories of week-long stays in with enormous, of dinnertime at Scout camp spent at picnic tables beneath an expansive overhang of massive logs, or the dusky windows and rooflines of a tucked-away hotel partially hidden in the pines.This architectural trend, informally called “Parkitecture,” was developed a century ago as railroads spread west and takes its design cue from the shelters at national parks such as Yosemite, Yellowstone, or Zion, as well as from the in the East. Today’s buyers are trying to re-create the look by asking log companies to incorporate large-diameter logs, chinking, timber, and grand entries into their rustic-setting homes. And for those who are nearing retirement, and can invest in a luxurious vacation home, the nostalgic lodges of the past act as guide to what looks natural, massive and successful in the rough terrain. Their desire to live in the mountains and close to nature is being satisfied by land developers who provide roads and services to these remote areas. Parkitecture.
Please follow if you have any high-quality images that you can contribute to the website. Step 1: general advice.Patients with only a few AMN, which have not changed and in the absence of a family history of melanoma, do not need referring.Such patients need to be taught on.Patients should take photographs of their moles and store the images on a home computer - the patient and partner / relative should perform a skin examination every three months and compare against the images to look for changeStep 2: a routine referral to a dermatologist is recommended for patients with the following:.Larger numbers of AMN.Very large numbers of moles, both typical and atypical in appearance. The term Atypical Mole syndrome (AMS) is used to define patients who have very large numbers of moles (at least 50), at least two of which appear atypical. Patients with AMS have approximately a 3% risk of developing a melanoma de novo.The Familial Atypical Mole and Melanoma syndrome (FAMM) - this is defined by patients with large numbers of typical and atypical melanocytic lesions AND a family history of melanoma in one or more 1st or 2nd degree relatives.
These patients usually have an increased number of typical melanocytic naevi appearing in childhood, with AMN first appearing in adolescence. The total number of naevi is relatively stable by the end of puberty and is often more than 50. Such patients have a very high risk of melanoma (RR 100-400) and require long-term follow up by a dermatologistStep 3: an urgent 2 Week Rule referral to a dermatologist is recommended for patients with the following:.Any 'atypical mole' which is changing in size, shape or colour.Any atypical lesions causing diagnostic uncertainty.